Advances in SNP based phylogenomics
Kunming Institute of Botany, 2019
Deren Eaton, Columbia University
The goal of phylogenomics
Characterize evolutionary relationships from a subset of sampled genomes.
WGS vs. RAD-seq genomic sampling
Characterize whole genomes from a subset of sequenced markers.
Coalescent variation
Different genomic regions have different genealocial histories.
Can sparse SNP sampling reconstruct
genome-wide patterns?
Filtering and formatting to deal with missing data...

Outline: RAD-seq phylogenomics in ipyrad
1. ipyrad-analysis toolkit.
2. Gene tree extraction: concatenation.
3. Gene tree distributions: sliding window consensus.
4. Sticking with SNPs: genome-wide inference.
ipyrad-analysis toolkit (and toytree) and jupyter
ipyrad-analysis toolkit
Filter or impute missing data; easily distribute massively parallel jobs.
import ipyrad.analysis as ipa
# initiate an analysis tool with arguments
tool = ipa.pca(data=data, ...)
# run job (distribute in parallel)
tool.run()
# examine results
...
Quercus section Virentes
35 samples, 7 species plus outgroups.
ipyrad (ref): 58K loci, 51% missing, 484K SNPs. (30 min., 40 cores).
Hipp et al. (2014); Eaton et al. (2015); Cavender-Bares et al. (2015)
PCA: very sensitive to missing data
PCA: very sensitive to missing data
PCA: clear delimitation when (some) data are imputed
Outline: RAD-seq phylogenomics in ipyrad
1. ipyrad-analysis toolkit.
2. Gene tree extraction: concatenation.
3. Gene tree distributions: sliding window consensus.
4. Sticking with SNPs: genome-wide inference.
Missing data in phylogenetics
Missing data in phylogenetics
Missing data in phylogenetics
Window_extracter: extract, filter, format.
Reference mapped RAD loci can be "spatially binned" to form larger loci.
import ipyrad.analysis as ipa
# initiate an analysis tool with arguments
tool = ipa.window_extacter(
data=data,
scaffold_idx=0,
start=0,
end=1000000,
)
# writes a phylip file
tool.run()
Window_extracter: extract, filter, format.
Reference mapped RAD loci can be "spatially binned" to form larger loci.
Window_extracter: extract, filter, format.
Reference mapped RAD loci can be "spatially binned" to form larger loci.
Herbicide resistance among Amaranthus species.
Missing data in phylogenetics
Missing data in phylogenetics
Goal: A distribution of gene trees representing every species.
Missing data: Consensus sampling
Represent species by the consensus genotype across sampled individuals
treeslider: extract windows across chromosomes.
Runs raxml on windows and parses results into a "tree_table"
# define population groups
imap = {
"sp1": ["a0", "a1", "a2", "a3"],
"sp2": ["b0", "b1", "b2", "b3"],
"sp3": ["c0", "c1", "c2", "c3"],
"sp4": ["d0", "d1", "d2", "d3"],
}
# initiate an analysis tool with arguments
tool = ipa.treeslider(
data=data,
window_size=1e6,
slide_size=1e6,
imap=imap,
)
# distributes raxml jobs across all 1M windows in data set
tool.run()
Consensus sampling yields 3X as many fully sampled loci.
One sample of each species: 12K/57K loci
Consensus for each species: 32K/57K loci
Hipp et al. (2014); Eaton et al. (2015); Cavender-Bares et al. (2015)
Sliding windows
How well do concatenated RAD windows represent gene tree variation?
RAxML gene trees.
Sliding windows
How well do concatenated RAD windows represent gene tree variation?
Astral species trees inferred from gene trees.
Clade weights (sensu Martin et al. 2017)
Chrom 1 weighted support for a (Cuba, Florida) vs (Cuba, Mexico)
Missing data in phylogenetics
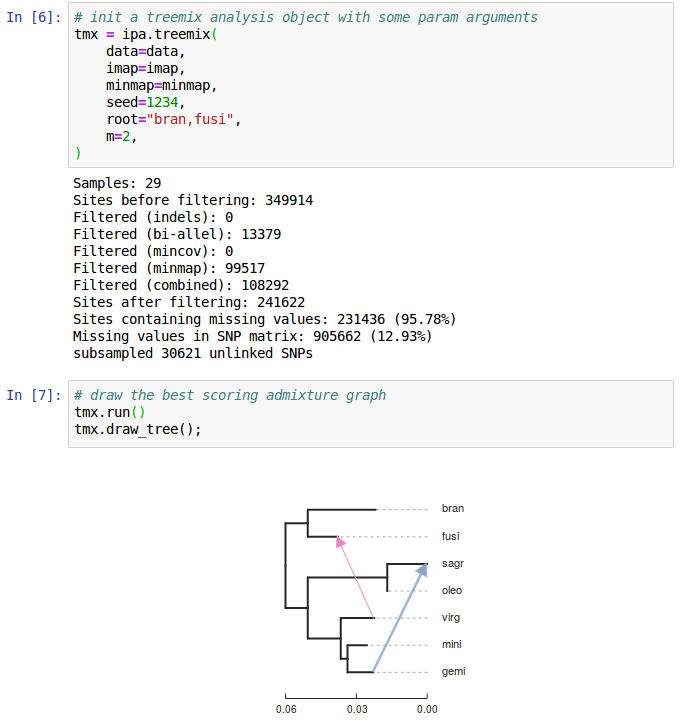
SNP-based species trees
SNAPP: joint inference of gene trees and species trees.
(Bryant et al. 2012)
SVDquartets: infers quartet trees from SNPs and joins these into a species tree.
(Chifman and Kubatko 2014)
Advantages to SVDquartets-based methods
Each quartet is inferred independently: missing data has almost no effect.
It is fast! My software tool, tetrad is even much faster.
e.g., Guo Cen applied tetrad to infer a 218 species tree for Arundinarieae

What are the next frontiers in SNP based inference?
1. Faster methods for integrating over SNPs to infer species trees (i.e., faster-SNAPP)
2. Network inference by integrating over SNPs (i.e., SNP-based-phylonet)
3. Network inference from SNP

Patrick McKenzie
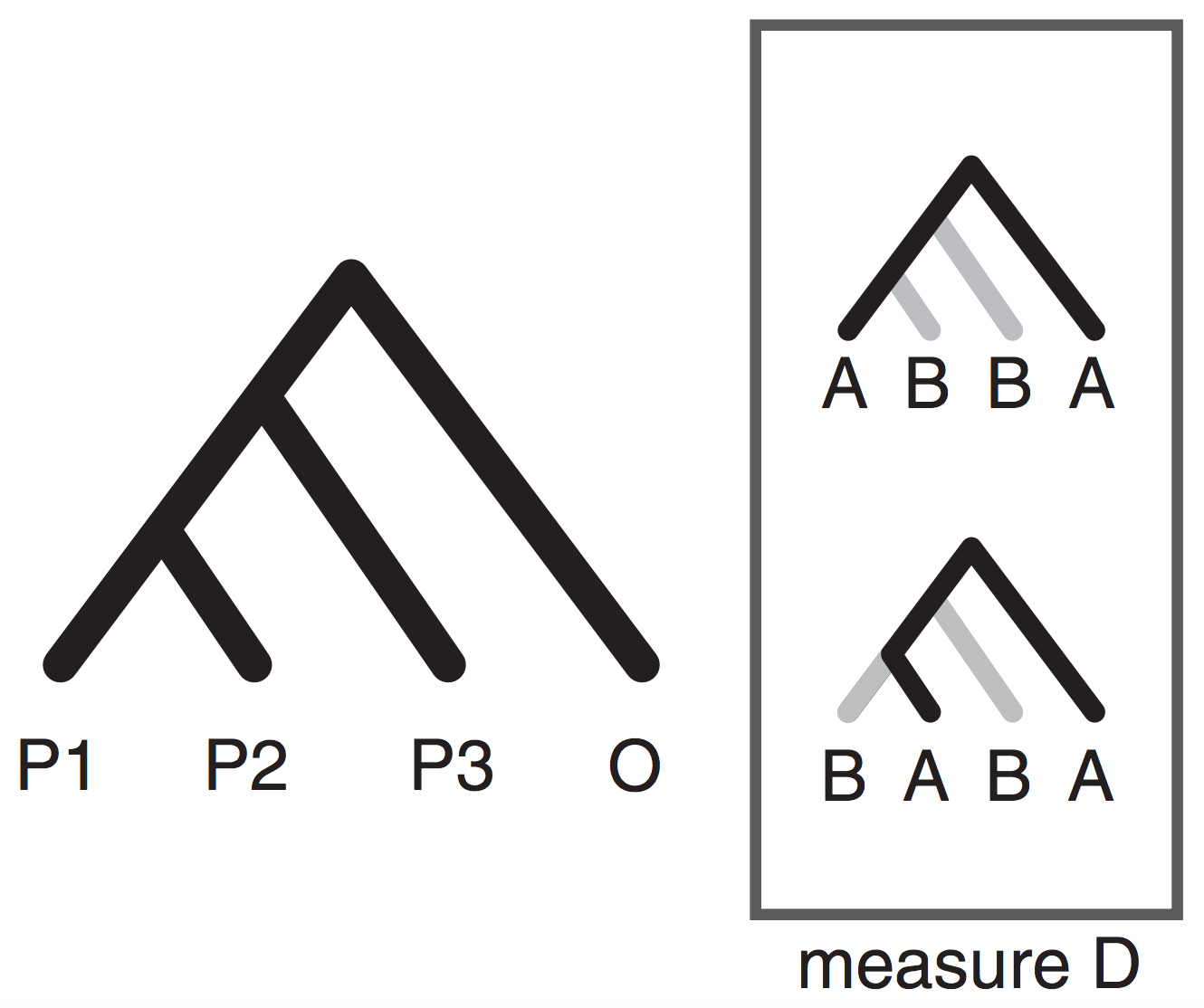
Background of SVDquartets
SVDquartets orders SNP patterns among quartet samples into 3 matrices.
One contains more patterns matching the tree (e.g., AABB)
Two contain patterns discordant with the tree (e.g., BABA, ABBA)
The matrix matching the tree aligns along rows/cols.
SVD decomposition measures matrix filling, and quickly finds best tree.
However...
SVDquartets discards the other two subtrees which contain
information relevant to inferring admixture (e.g., ABBA-BABA imbalance)
(Durand et al. 2011)
In addition...
SVDquartets only examines individual quartets at a time
Because quartets are not independent of each other, introgression of one
may affect multiple other quartets (Eaton et al. 2012, 2015).
Ideally, all taxa, or all quartets, would be examined simultaneously.
Joint inference of all quartet matrices for network inference

SVDquartets reduces SNP matrices to categorical results
SVDquartets reduces SNP matrices to categorical results
SVDquartets reduces SNP matrices to categorical results
SVDquartets reduces SNP matrices to categorical results
SVDquartets reduces SNP matrices to categorical results
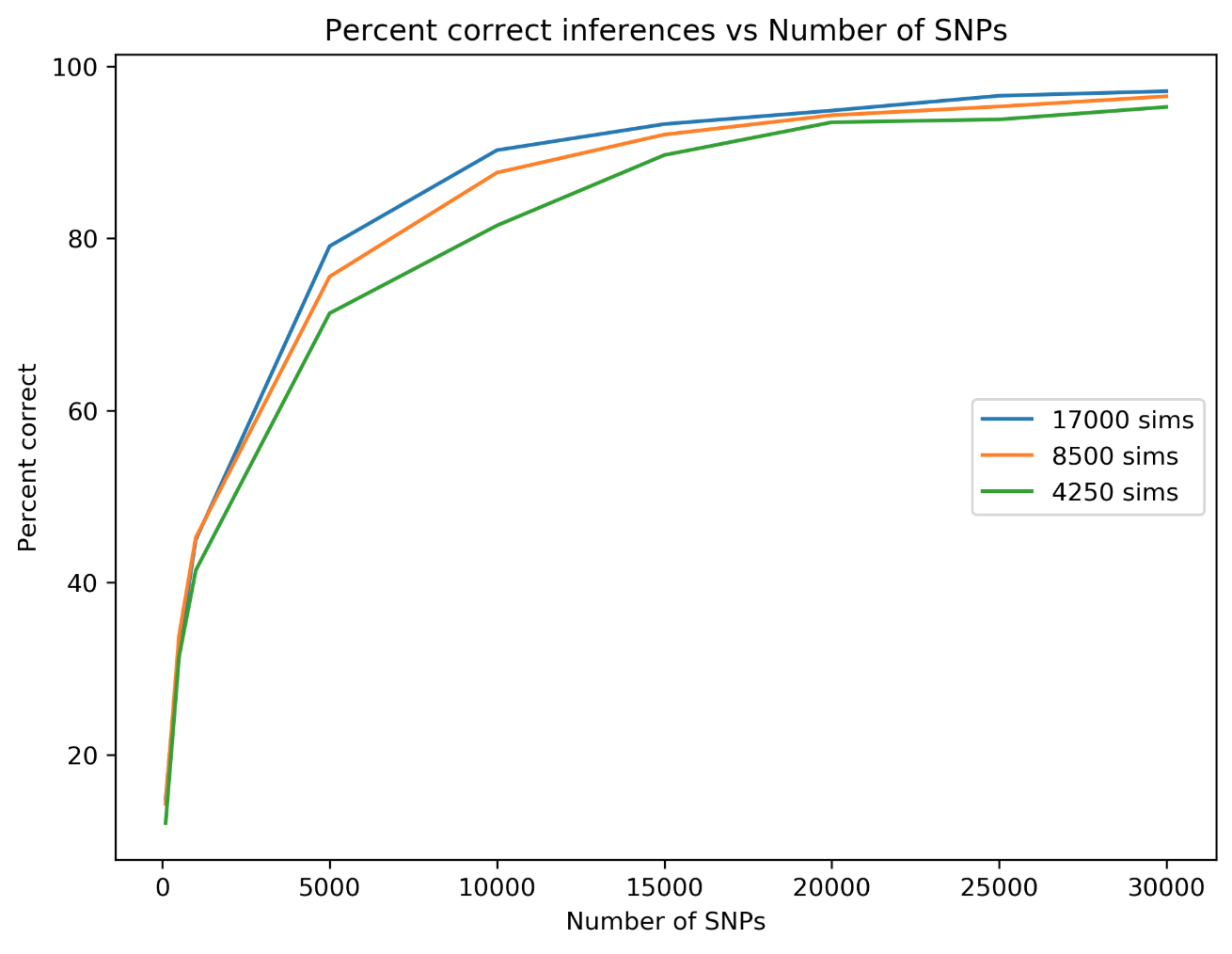
Stacked count matrices
Unique fingerprint for different admixture scenarios
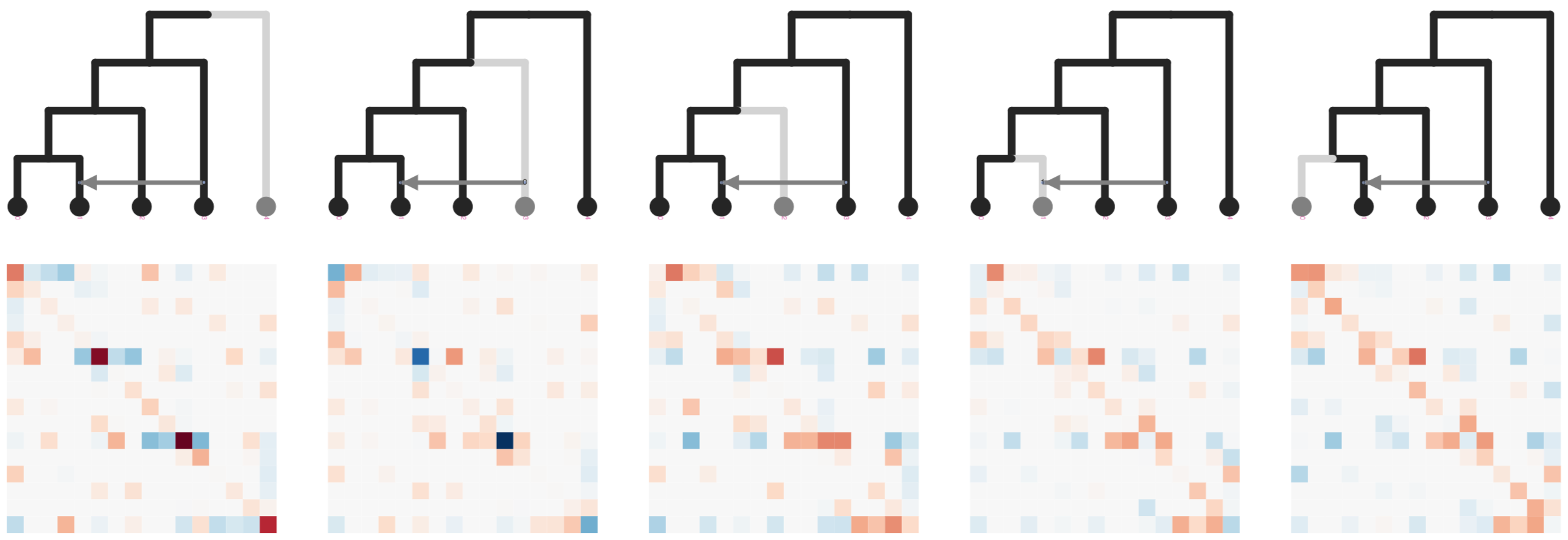
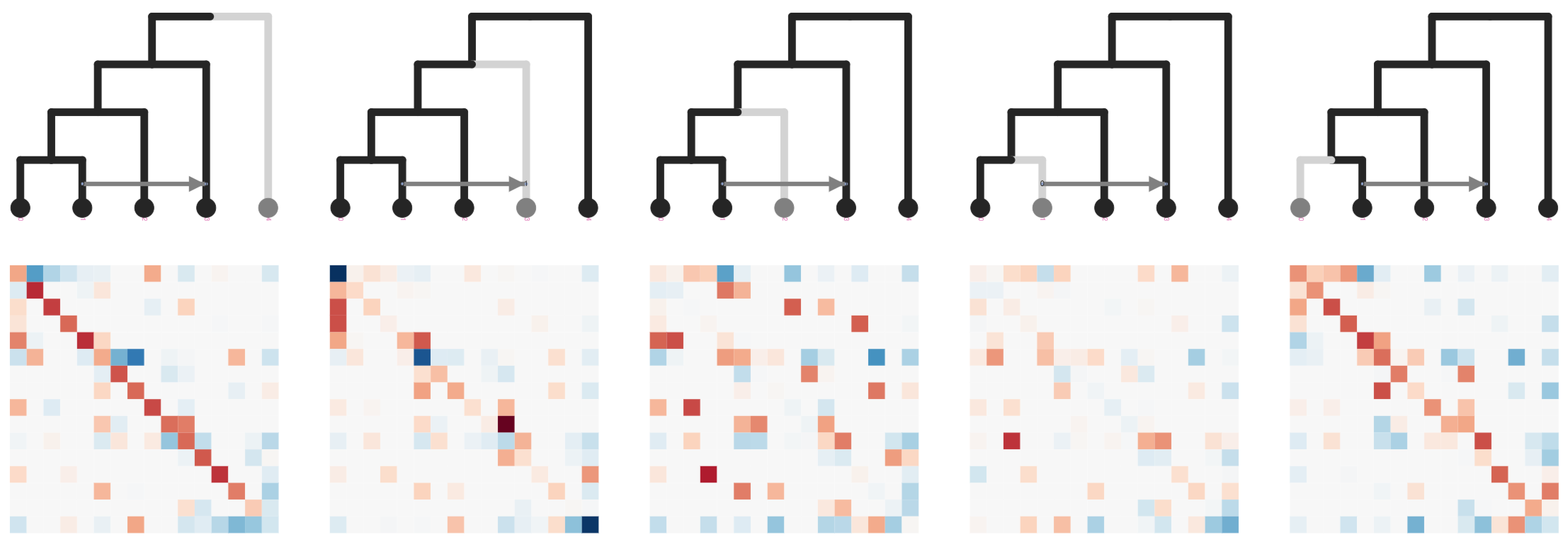
Simulate SNP data on a tree, train ML model on admixture scenario
ExtraTrees Classifier (scikit-learn)
Conclusions
1. With ipyrad-analysis it is easy to run dozens of analyses optimized for RAD missing-ness with a few lines of code.
2. Concatenating RAD loci in scaffold windows, and consensus or imputation sampling, dramatically improve the utility of RAD.
3. SNP based methods are in their infancy, but work well with RAD data.
Acknowledgements
Oaks data set:
Jeannine Cavender-Bares
Andrew Hipp
Antonio Gonzalez-Rodriguez
ipyrad development:
Isaac Overcast
Eaton lab members
Funding:
NSF DEB 1557059
Columbia University
Questions?
RADcamp wetlab and bioinformatics workshop in New York City Oct. 2019
Bring your DNA samples.
Library preparation and sequencing will be free.
(sponsored by SSB, Columbia, CCNY).