Phylogenomic Perspectives on Reproductive
Isolation and Introgression
Deren Eaton, Columbia University
Botany 2019, Tucson
Outline: Plant Perspectives
1. Phylogenomic data generation
2. Species tree inference
3. Network/admixture inference
4. Reproductive isolation and phylogenomics
5. Advances on the horizon...
Generating data: reference genomes
Quality reference genome assemblies are now generally obtainable.
Generating data: reference genomes
Quality reference genome assemblies are now generally obtainable.
> Long read technologies (e.g., Oxford Nanopore)
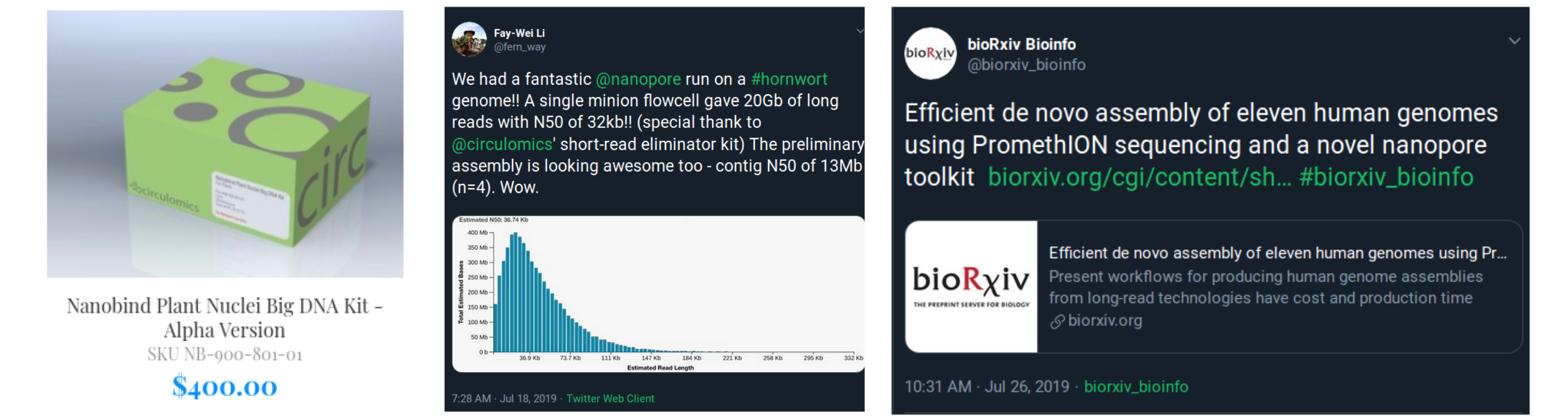
Generating data: reference genomes
Quality reference genome assemblies are now generally obtainable.
> Long range scaffolding technologies (e.g., Chicago, Hi-C)
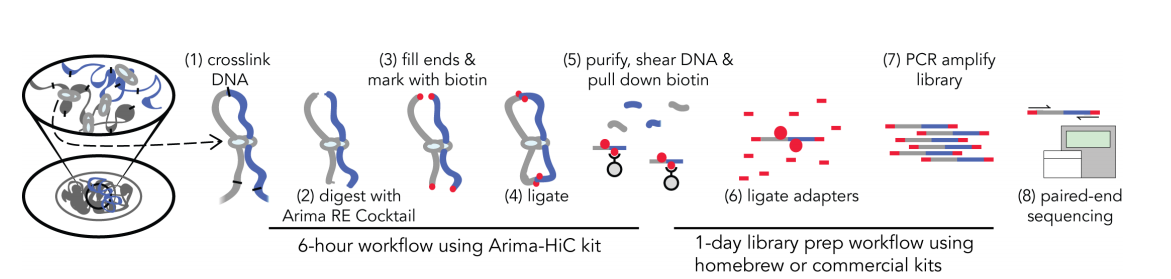
Generating data: reference genomes
Caveat: requires large(ish) quantities of (fresh/flash frozen) leaf tissue.

Generating data: reference genomes
Caveat: requires large(ish) quantities of (fresh/flash frozen) leaf tissue.

Generating data: phylogenetic markers
1. WGS-reseq: relatively affordable, future of shallow-scale.
2. RAD-seq: affordable for shallow-scale or many many samples.
3. Target-capture: Bread and butter for deep-scale.
Outline: Plant Perspectives
1. Phylogenomic data generation
2. Species tree inference
3. Network/admixture inference
4. Reproductive isolation and phylogenomics
5. Advances on the horizon...
Coalescent variation
Different genomic regions have different genealogical histories.
Coalescent variation
Different genomic regions have different genealogical histories.
Advances in species tree inference
Joint gene tree & species tree inference (e.g., *BEAST, BPP)
Summary inference based on gene-tree inputs (e.g., ASTRAL)
Quartet joining with fast inference from SNPS (e.g., SVDQuartets)
Outline: Plant Perspectives
1. Phylogenomic data generation
2. Species tree inference
3. Network/admixture inference
4. Reproductive isolation and phylogenomics
5. Advances on the horizon...
Coalescent variation within a network
Different genomic regions have different genealogical histories.
Advances in network inference
Summary inference based on gene-tree inputs (e.g., Phylonet, SNAQ)
Joint gene tree & network inference (e.g., Phylonet, BEAST2)
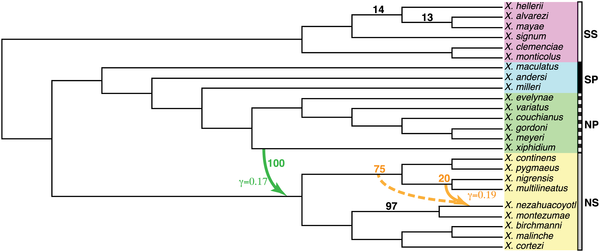
Coalescent variation within a network
Different genomic regions have different genealogical histories.
Coalescent variation within a network
Different genomic regions have different genealogical histories.
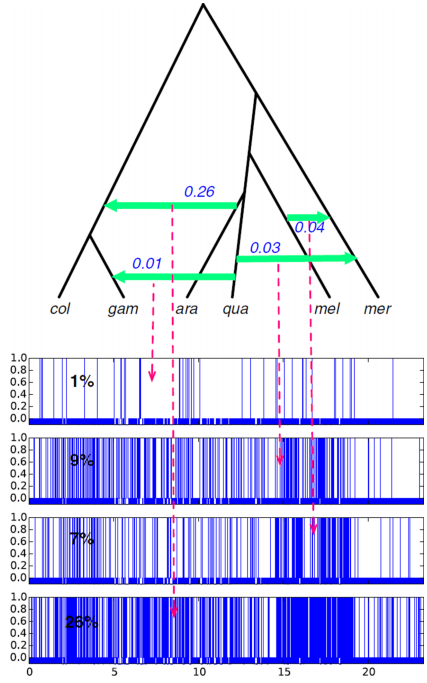
Wen et al. (2016)
Outline: Plant Perspectives
1. Phylogenomic data generation
2. Species tree inference
3. Network/admixture inference
4. Reproductive isolation and phylogenomics
5. Advances on the horizon...
Introgression in the context of biology
Are introgressive patterns concordant with reproductive traits, or geography?
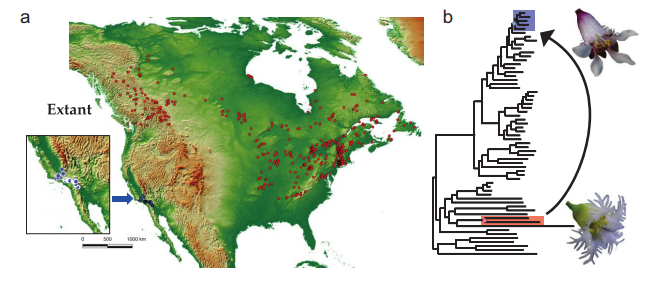
Folk et al. (2018)
Introgression in the context of biology
Sliding windows can reveal interplay of introgression and selection
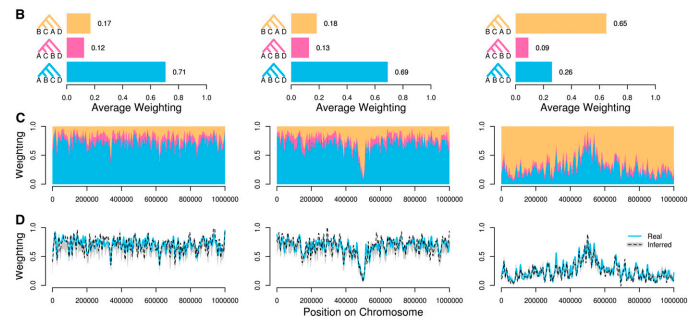
Martin et al. (2017)
Outline: Plant Perspectives
1. Phylogenomic data generation
2. Species tree inference
3. Network/admixture inference
4. Reproductive isolation and phylogenomics
5. Advances on the horizon...
A disconnect between theory and practice
Sliding windows reveal genealogical variation; but what is our expectation?
Species tree/network models could provide a better null.
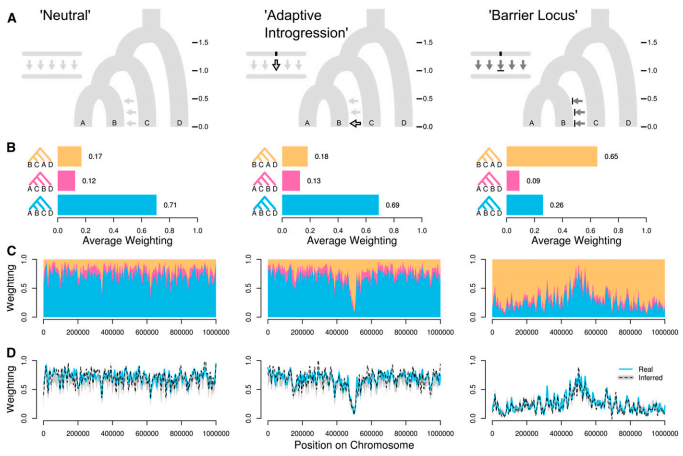
Martin et al. (2017)
Additional sources of information.
Recombination rate are correlated with retention of introgressed blocks
But such data are not readily available for many taxa...
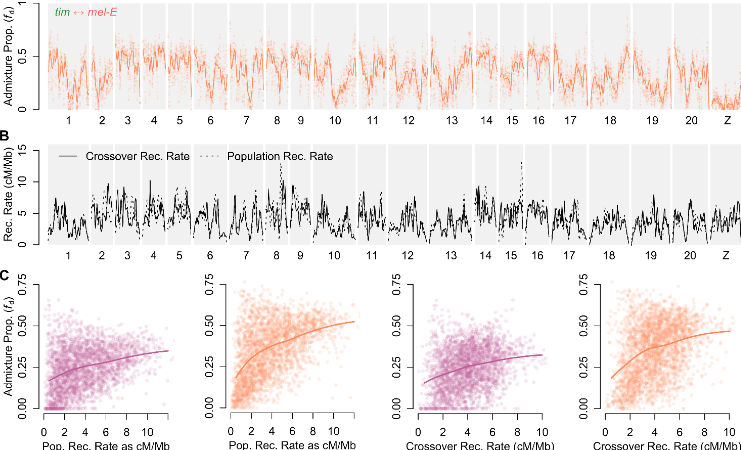
Martin et al. (2019)
Phylogenomic Perspectives on Reproductive
Isolation and Introgression
Conclusions:
> Increased availability of genome-wide comparative data
> Hierarchical model inference (e.g., species trees/networks)
> Spatial investigation (e.g., sliding windows)
> Introgression in the context of biology (traits, geography, selection)
> Combining spatial and hierarchical models
Phylogenomic Perspectives on Reproductive
Isolation and Introgression
